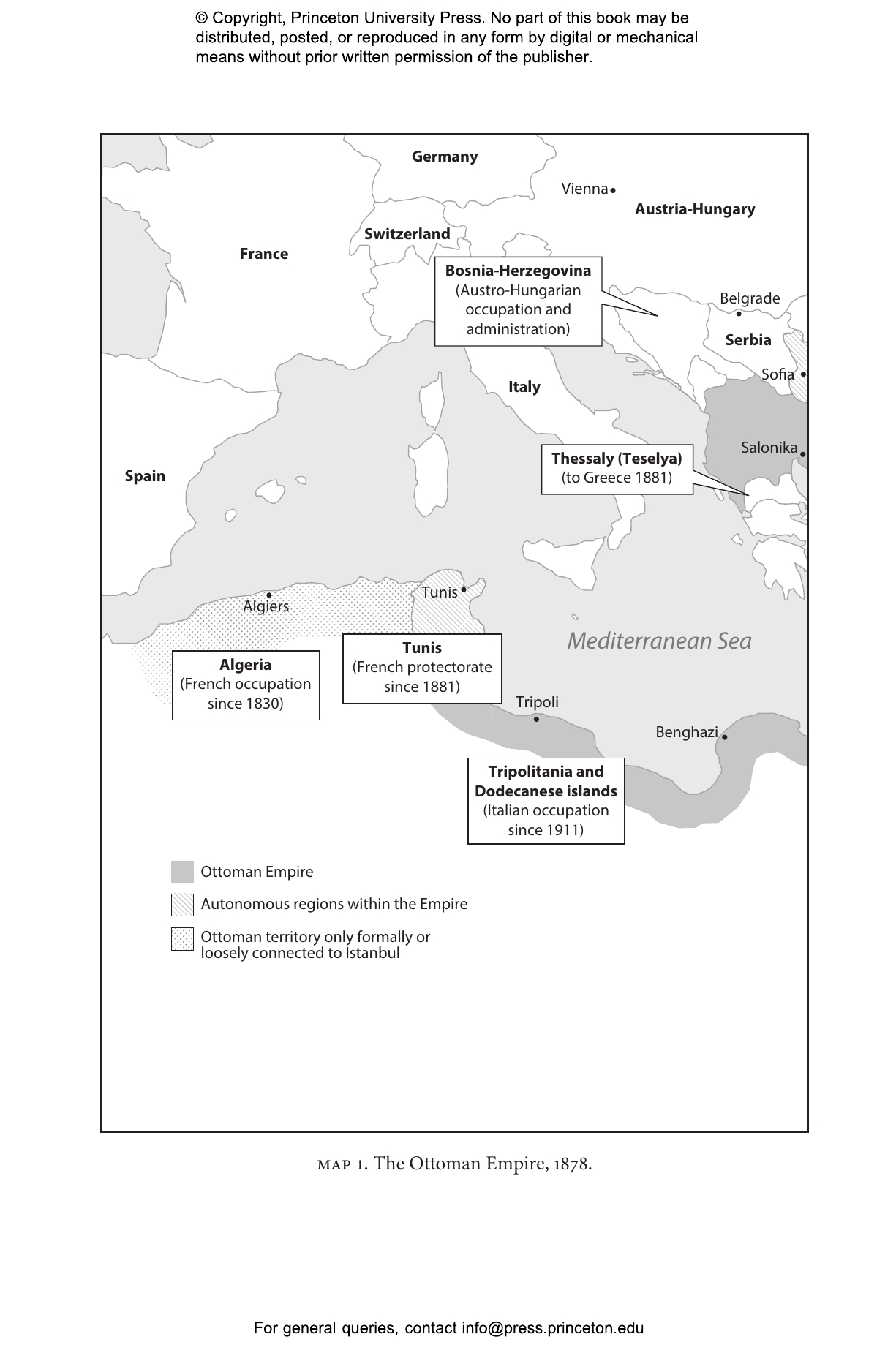
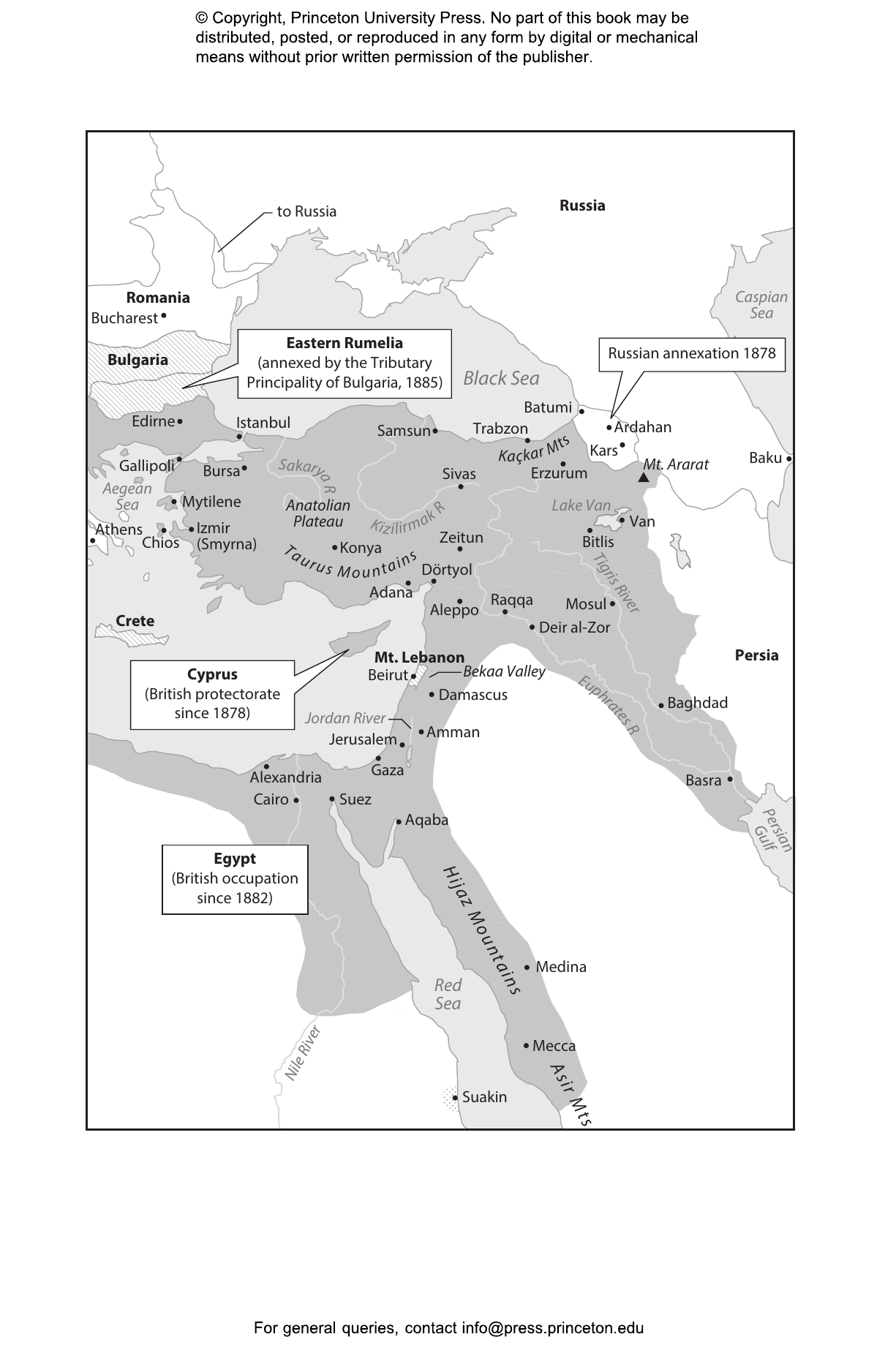
The Ottoman EmpireÔÇÖs collapse at the end of the First World War is often treated as a foregone conclusion. It was only a matter of time, the story goes, before the so-called Sick Man of Europe succumbed to its ailmentsÔÇöincompetent management, nationalism, and ethnic and religious conflict. In The War That Made the Middle East, Mustafa Aksakal overturns this conventional narrative. He describes how European imperial ambitions and the Ottoman commitment to saving its empire at any costÔÇöincluding the destruction of the Armenian community and the deaths of more than a million Ottoman troops and other civiliansÔÇöled to the empireÔÇÖs violent partition and created a politically unstable Middle East.
The War That Made the Middle East shows that, until 1914, the Ottoman Empire was a viable multiethnic, multireligious state, and that relations between the Arabs, Jews, Muslims, and Christians of Palestine were relatively stable. When war broke out, the Ottoman government sought an alliance with the Entente but was rejected because of British and French designs on the Eastern Mediterranean. After the Ottomans entered the fight on the side of Germany and were defeated, Britain and France seized Ottoman lands, and new national elites in former Ottoman territories claimed their own states. The region was renamed ÔÇťthe Middle East,ÔÇŁ erasing a robust and modernizing 600-year-old empire.
A sweeping narrative of war, great power politics, and ordinary people caught up in the devastation, The War That Made the Middle East offers new insights about the Great War and its profound and lasting consequences.
Mustafa Aksakal is associate professor of history and the Nesuhi Erteg├╝n Chair of Modern Turkish Studies at Georgetown University. He is the author of The Ottoman Road to War in 1914: The Ottoman Empire and the First World War.
33922
“This is a landmark new history of the origins of war and dictatorship in the modern Middle East. Mustafa Aksakal deploys an astonishing breadth of research to weave a tragic story about the disastrous choices made by Ottoman rulers confronting existential threats during World War I. He shows how the Ottoman Empire, like so many other states, destroyed its own people in a war against both external imperialists and internal opponents. A must-read for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of the Armenian Genocide, Islamic politics, Middle Eastern dictatorship, and the region’s ongoing trauma.”—Elizabeth F. Thompson, author of How the West Stole Democracy from the Arabs
“The War That Made the Middle East explores the Ottoman Empire’s struggle to preserve its beleaguered sovereignty and reconstitute itself through the crucible of the First World War. Offering a corrective to Eurocentric diplomatic accounts, deterministic national histories of successor states, and reductionist genocide-centered narratives, Aksakal draws on rare Ottoman archival materials and overlooked German sources to illuminate the complexity of a transformative war.”—Hasan Kayali, author of Imperial Resilience: The Great War’s End, Ottoman Longevity, and Incidental Nations
“Few wars have more profoundly affected the future than World War I. Mustafa Aksakal, the leading expert on the final struggles of the Ottoman Empire, demonstrates in clear, powerful prose that the Young Turk radicals who seized control of the empire on the eve of the war were the architects of Ottoman destruction. Going deeper than diplomatic or military history, Aksakal grounds his book in the social realities and misperceptions that led Ottoman leaders to kill hundreds of thousands of their Armenian and Assyrian subjects in a desperate, ill-conceived fight against perceived internal enemies.”—Ronald Grigor Suny, author of “They Can Live in the Desert but Nowhere Else”: A History of the Armenian Genocide
This publication has been produced to meet accepted Accessibility standards and contains various accessibility features including concise image descriptions, a table of contents, a page list to navigate to pages corresponding to the print source version, and elements such as headings for structured navigation. Appearance of the text and page layout can be modified according to the capabilities of the reading system.
Accessibility Features
-
WCAG v2.2
-
WCAG level AA
-
Table of contents navigation
-
Single logical reading order
-
Short alternative textual descriptions
-
Print-equivalent page numbering
-
Landmark navigation
-
Index navigation
-
Epub Accessibility Specification 1.1
-
ARIA roles provided
-
All non-decorative content supports reading without sight
-
No known hazards or warnings